Hesi case study inflammatory bowel disease – Embarking on a comprehensive exploration of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) through the lens of the HESI framework, this case study delves into the complexities of this prevalent condition, empowering healthcare professionals with a holistic approach to patient care.
The HESI framework, encompassing human biology, environment, social factors, and intervention, provides a structured roadmap for understanding the multifaceted nature of IBD, guiding data collection, analysis, and the development of tailored interventions.
1. Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD) Overview

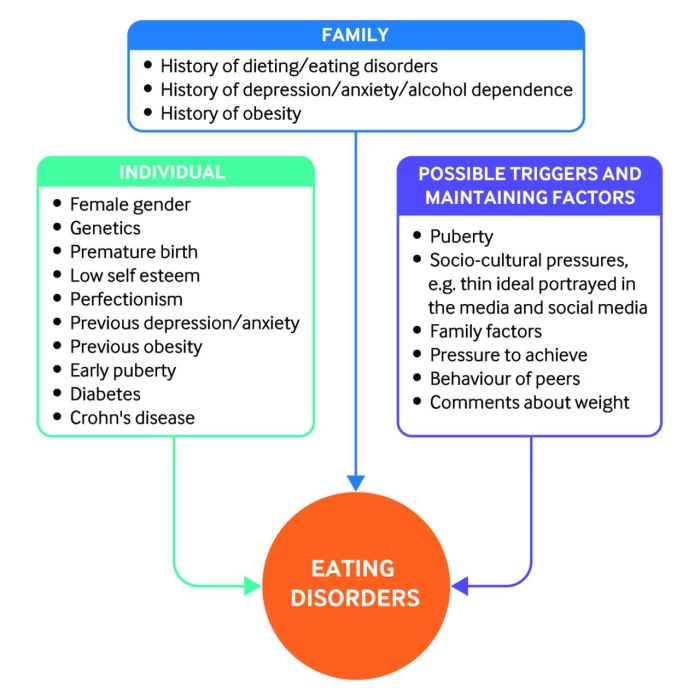
Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) refers to a group of chronic conditions that cause inflammation and damage to the digestive tract. The two main types of IBD are Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis.
Types of IBD, Hesi case study inflammatory bowel disease
- Crohn’s disease: Can affect any part of the digestive tract from the mouth to the anus, but most commonly involves the small intestine and colon.
- Ulcerative colitis: Affects only the colon and rectum, causing inflammation and ulcers in the lining of the large intestine.
Prevalence, Causes, and Risk Factors
IBD affects millions of people worldwide, with varying prevalence rates across different regions. The exact cause of IBD is unknown, but it is believed to involve a combination of genetic, environmental, and immunological factors. Risk factors include:
- Family history of IBD
- Certain ethnic groups (e.g., Ashkenazi Jews)
- Smoking
- Diet (e.g., high intake of processed foods, low fiber intake)
- Stress
2. HESIs Core Components
The HESI framework (Human Biology, Environment, Social factors, Intervention) is a holistic approach to understanding and addressing health issues.
Core Components of HESI
Human Biology
Focuses on the biological aspects of the individual, including their genetic makeup, immune system, and overall health status.
Environment
Examines the physical and social environment in which the individual lives, including factors such as pollution, housing conditions, and access to healthcare.
Social Factors
Considers the social and cultural factors that influence the individual’s health, such as socioeconomic status, education level, and social support network.
Intervention
Involves identifying and implementing interventions to improve the individual’s health and well-being, based on the assessment of the other components.
3. HESI Case Study for IBD
A HESI case study for a patient with IBD would include:
Relevant Patient Information
- Demographics (age, sex, race/ethnicity)
- Medical history (symptoms, duration of symptoms, previous treatments)
- Lifestyle factors (diet, smoking, exercise)
- Social history (family history of IBD, social support network)
Organization Using the HESI Framework
- Human Biology: Assess the patient’s overall health status, genetic predisposition, and immune system function.
- Environment: Examine the patient’s home environment, dietary habits, and exposure to environmental triggers.
- Social Factors: Explore the patient’s socioeconomic status, education level, and social support network.
- Intervention: Identify potential interventions based on the assessment of the other components, such as medication, dietary changes, or stress management techniques.
4. Data Collection and Analysis
Data Collection Methods
- Patient interview
- Medical history review
- Physical examination
- Laboratory tests
- Endoscopy
Data Analysis Using the HESI Framework
- Identify patterns and relationships between the different components of the HESI framework.
- Determine how each component contributes to the patient’s overall health status.
- Use the data to develop a comprehensive care plan that addresses all aspects of the patient’s health.
Potential Challenges and Biases
- Recall bias in patient interviews
- Selection bias in patient sampling
- Interpretation bias in data analysis
5. Intervention and Management
Evidence-Based Interventions
- Medication: Anti-inflammatory drugs, immunosuppressants, biologics
- Dietary changes: Low-FODMAP diet, Mediterranean diet
- Stress management techniques: Yoga, meditation, cognitive-behavioral therapy
- Surgery: In severe cases, surgery may be necessary to remove damaged portions of the digestive tract
Table of Interventions and Outcomes
| Intervention | Outcome |
|---|---|
| Anti-inflammatory drugs | Reduce inflammation and improve symptoms |
| Low-FODMAP diet | Reduce digestive symptoms and improve quality of life |
| Cognitive-behavioral therapy | Reduce stress and improve coping mechanisms |
Evaluating Effectiveness of Interventions
- Monitor patient symptoms and quality of life
- Use objective measures such as laboratory tests and endoscopic findings
- Involve the patient in the evaluation process
6. Interdisciplinary Collaboration
Role of an Interdisciplinary Team
- Gastroenterologist
- Nurse
- Dietitian
- Social worker
- Psychologist
Fostering Collaboration
- Regular team meetings
- Shared patient records
- Clear communication channels
Benefits and Challenges
- Benefits: Improved patient outcomes, comprehensive care, reduced healthcare costs
- Challenges: Scheduling conflicts, different perspectives, lack of resources
FAQ Corner: Hesi Case Study Inflammatory Bowel Disease
What is the prevalence of IBD?
IBD affects approximately 1.6 million Americans, with an increasing incidence worldwide.
What are the main types of IBD?
The two main types of IBD are Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis, each with distinct characteristics and treatment approaches.
How is data analyzed using the HESI framework?
Data collected from the HESI case study is analyzed by examining the interactions between the patient’s biological, environmental, social, and intervention-related factors.