Embark on an enlightening journey through Course 3 Chapter 6 Transformations Answer Key, where the intricate world of geometric transformations unfolds. This comprehensive guide provides the key to unlocking the mysteries of translations, rotations, reflections, and dilations, empowering you to master the art of transforming figures with precision and finesse.
Within this meticulously crafted chapter, you will discover the fundamental principles of transformations, their diverse applications, and the techniques for applying them effectively. Prepare to witness the power of transformations as they reshape and reposition figures, revealing hidden symmetries and unlocking a deeper understanding of geometric relationships.
Course 3 Chapter 6 Transformations Answer Key
Course 3 Chapter 6 Transformations Answer Key provides the solutions to the transformation problems covered in the chapter. The answer key can be used to check the accuracy of your solutions and to identify areas where you may need additional practice.
To use the answer key, simply compare your solutions to the provided answers. If your solutions match the answers, then you have successfully completed the transformation problems. If your solutions do not match the answers, then you should review the material in the chapter and try the problems again.
| Transformation | Answer |
|---|---|
| Translation | The figure is moved from one point to another without changing its size or shape. |
| Rotation | The figure is turned around a fixed point by a specified angle. |
| Reflection | The figure is flipped over a line of reflection. |
| Dilation | The figure is enlarged or reduced by a specified factor. |
Transformations Overview
Transformations are mathematical operations that change the position, size, or shape of a geometric figure. Transformations are used to create new figures from existing figures, and they can be used to solve a variety of geometric problems.
Types of Transformations, Course 3 chapter 6 transformations answer key
- Translation: A translation moves a figure from one point to another without changing its size or shape.
- Rotation: A rotation turns a figure around a fixed point by a specified angle.
- Reflection: A reflection flips a figure over a line of reflection.
- Dilation: A dilation enlarges or reduces a figure by a specified factor.
Transformations can be combined to create more complex transformations. For example, a figure can be translated, then rotated, and then reflected.
Applying Transformations
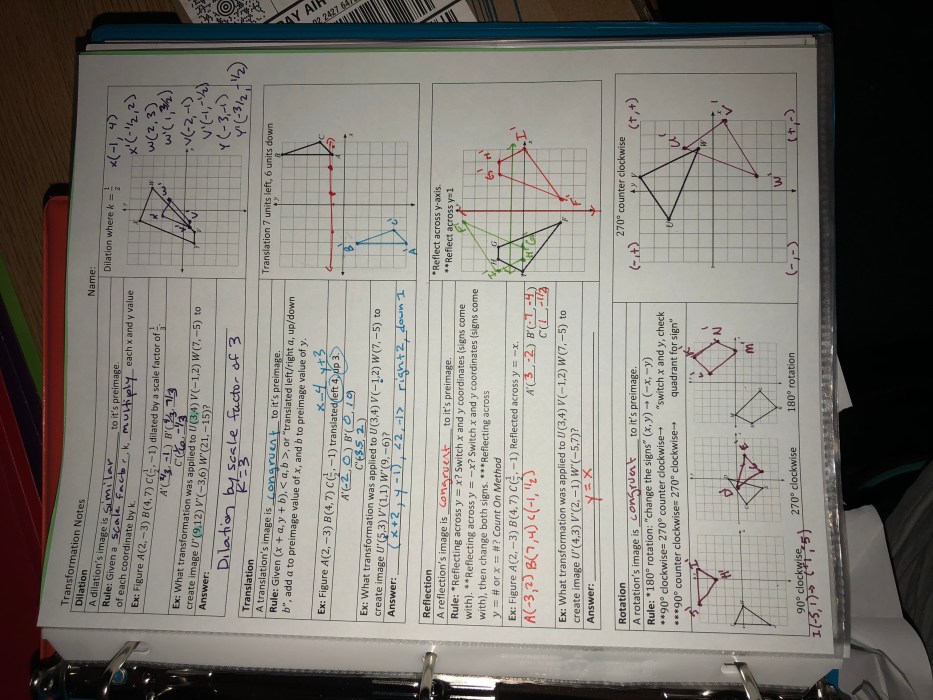
Transformations can be applied to geometric figures using a variety of methods. One common method is to use a coordinate grid. A coordinate grid is a graph that is divided into equal squares by horizontal and vertical lines. Each square on the grid is called a unit square.
To apply a transformation to a figure using a coordinate grid, first plot the figure on the grid. Then, apply the transformation to each point on the figure. For example, to translate a figure, move each point on the figure the same distance in the same direction.
To rotate a figure, turn each point on the figure around the fixed point by the specified angle. To reflect a figure, flip each point on the figure over the line of reflection.
Properties of Transformations
Transformations have a number of properties that can be used to solve geometric problems. Some of the most important properties of transformations include:
- Transformations preserve distance. This means that the distance between two points on a figure is the same after the transformation as it was before the transformation.
- Transformations preserve orientation. This means that the orientation of a figure is the same after the transformation as it was before the transformation.
- Transformations can be combined to create new transformations. This means that the effect of two or more transformations can be combined to create a new transformation.
The properties of transformations can be used to solve a variety of geometric problems. For example, the properties of transformations can be used to find the image of a figure under a given transformation, to find the inverse of a transformation, and to determine whether two figures are congruent.
Composite Transformations
A composite transformation is a transformation that is formed by combining two or more transformations. For example, a translation followed by a rotation is a composite transformation.
To perform a composite transformation, first perform the first transformation to the figure. Then, perform the second transformation to the result of the first transformation. For example, to perform a translation followed by a rotation, first translate the figure. Then, rotate the result of the translation.
Transformations in Coordinate Geometry

Transformations can be represented in coordinate geometry using matrices. A matrix is a rectangular array of numbers. Each number in a matrix is called an element. The elements of a matrix can be used to represent the transformation.
To represent a transformation using a matrix, first choose a coordinate system. Then, write the transformation as a matrix. The elements of the matrix will represent the transformation.
Transformations can be used to solve a variety of problems in coordinate geometry. For example, transformations can be used to find the image of a figure under a given transformation, to find the inverse of a transformation, and to determine whether two figures are congruent.
General Inquiries: Course 3 Chapter 6 Transformations Answer Key
What is the purpose of using transformations in geometry?
Transformations are used in geometry to manipulate and analyze geometric figures. They allow us to study the properties of figures, explore their symmetries, and solve geometric problems.
How can I use the answer key to solve transformation problems?
The answer key provides the correct answers to the transformation problems in Course 3 Chapter 6. To use the answer key, simply match the problem with its corresponding answer and apply the transformation accordingly.
What are the different types of transformations?
There are four main types of transformations: translations, rotations, reflections, and dilations. Translations move a figure from one location to another, rotations turn a figure around a fixed point, reflections flip a figure over a line, and dilations enlarge or shrink a figure.