A nurse is caring for a newborn immediately following birth, a critical and delicate time that requires specialized knowledge, compassion, and meticulous attention to detail. This narrative explores the comprehensive responsibilities of nurses in ensuring the well-being and safety of newborns during their initial hours of life.
From the moment of delivery, nurses initiate a thorough assessment of the newborn’s vital signs, physical attributes, and overall health status. This initial evaluation, including the Apgar score, provides valuable insights into the newborn’s immediate condition and any potential complications.
Newborn Assessment
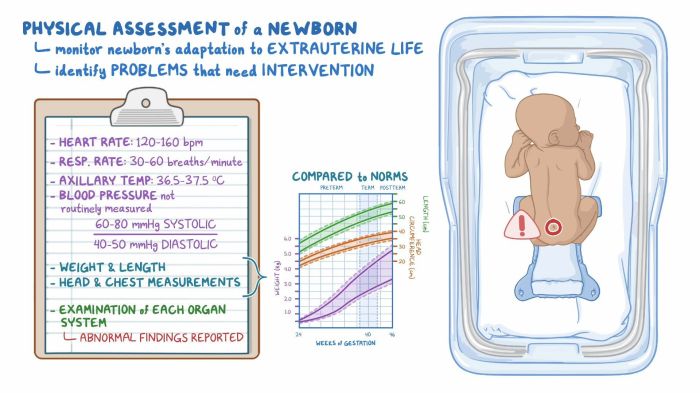
Immediately following birth, the newborn undergoes a thorough assessment to evaluate their overall health and well-being. This initial assessment includes monitoring vital signs, conducting a physical examination, and calculating the Apgar score.
Vital Signs
The newborn’s vital signs are closely monitored to ensure stability and identify any potential complications. These include:
- Temperature: Normal range is 97.6°F to 99.6°F (36.4°C to 37.6°C)
- Heart rate: Normal range is 120 to 160 beats per minute
- Respiratory rate: Normal range is 30 to 60 breaths per minute
- Oxygen saturation: Normal range is 95% or higher
Physical Examination
The newborn is examined head-to-toe to assess for any birth defects or abnormalities. This includes:
- Checking the head for any molding or caput succedaneum
- Examining the face for any facial paralysis or cleft lip/palate
- Assessing the spine for any spinal defects
- Checking the abdomen for any hernias or omphalocele
- Examining the genitalia for any abnormalities
Apgar Score, A nurse is caring for a newborn immediately following birth
The Apgar score is a quick and standardized assessment of the newborn’s overall condition at 1 and 5 minutes after birth. It is based on five criteria:
- Appearance (color)
- Pulse
- Grimace (reflex irritability)
- Activity
- Respiration
Each criterion is scored on a scale of 0 to 2, with a total score ranging from 0 to 10. A score of 7 or higher is considered reassuring.
Newborn Care

Providing proper care for a newborn immediately after birth is crucial for their health and well-being. This includes swaddling, feeding, and diaper changing.
Swaddling
Swaddling the newborn helps to provide warmth, comfort, and a sense of security. It also helps to prevent the Moro reflex, which can startle the newborn.
Feeding
The newborn should be fed within the first hour after birth. Breastfeeding is the recommended method of feeding, as it provides the newborn with the best nutrition and immune protection. If breastfeeding is not possible, formula can be used.
Diaper Changing
The newborn should be diaper changed frequently to prevent diaper rash. It is important to use gentle wipes and to avoid using harsh soaps or detergents.
Newborn Safety

Ensuring the safety of the newborn is of utmost importance. This includes creating a safe sleeping environment, bathing safely, and handling the newborn with care.
Safe Sleeping Environment
The newborn should sleep in a crib or bassinet with a firm mattress and no loose blankets or pillows. The newborn should be placed on their back to sleep.
Bathing Safely
The newborn should be bathed no more than once or twice a week. Use warm water and gentle soap. Support the newborn’s head and neck while bathing.
Handling the Newborn
Handle the newborn with care and support their head and neck at all times. Avoid shaking or tossing the newborn.
Newborn Monitoring
Monitoring the newborn for signs of distress or illness is essential for early detection and treatment. This includes monitoring their breathing, activity level, and feeding patterns.
Monitoring Breathing
The newborn’s breathing should be monitored closely. If the newborn is breathing rapidly, shallowly, or irregularly, it could be a sign of distress.
Monitoring Activity Level
The newborn should be active and alert. If the newborn is lethargic or unresponsive, it could be a sign of illness.
Monitoring Feeding Patterns
The newborn should feed regularly and with good appetite. If the newborn is not feeding well or is vomiting excessively, it could be a sign of illness.
Signs and Symptoms of Common Newborn Illnesses
Some common newborn illnesses include jaundice, sepsis, and respiratory distress syndrome. It is important to be aware of the signs and symptoms of these illnesses so that they can be treated promptly.
- Jaundice: Yellowing of the skin and eyes
- Sepsis: Fever, lethargy, and poor feeding
- Respiratory distress syndrome: Rapid breathing, grunting, and retractions
General Inquiries: A Nurse Is Caring For A Newborn Immediately Following Birth
What are the key responsibilities of a nurse caring for a newborn immediately after birth?
Nurses are responsible for conducting a comprehensive assessment of the newborn’s vital signs, physical attributes, and overall health status. They provide essential care, including swaddling, feeding, and diaper changing, while ensuring the newborn’s warmth and comfort. Additionally, nurses monitor the newborn for signs of distress or illness and implement appropriate interventions as needed.
How do nurses ensure the safety of newborns?
Nurses play a crucial role in creating a safe environment for newborns. They implement measures such as maintaining a clean and sterile environment, ensuring proper handling techniques to prevent falls, and educating parents on safe sleeping practices.
What are the common signs and symptoms of newborn illnesses that nurses should monitor for?
Nurses are trained to recognize and monitor for signs and symptoms of common newborn illnesses, including jaundice, sepsis, and respiratory distress syndrome. Early detection and intervention are essential for ensuring the well-being of newborns.